Epistemonikos summaries
← vista completaPublished on October 11, 2018 | http://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2018.06.7286
Cannabinoids for the treatment of cannabis abuse disorder
Cannabinoides para el tratamiento del trastorno por abuso de cannabis
Abstract
INTRODUCTION Cannabis stands as the most used illegal drug in the world. Currently there are no pharmacologic alternatives to treat its addiction, so the use of Cannabinoids has been postulated as a therapeutic tool. They would act mainly through decrease in abstinence and craving symptoms but its effectiveness remains unclear.
METHODS To answer this question we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS We identified seven systematic reviews including 15 studies, of which four were randomized trials. We concluded the use of cannabinoids might result in little or no increase in abstinence at the end of treatment, and it probably increases adverse effects.
Problem
Substance abuse disorder is an important epidemiological problem which is defined by the development of a maladaptive behavioral pattern in relation to the use of a substance and is usually accompanied by tolerance, one of the diagnostic elements of dependence. In this context, cannabis stands as one the most consumed illicit drugs, with addictive potential [1].
Even though there are no specific pharmacological alternatives to treat cannabis use disorders, diverse studies have postulated that the endocannabinoid system has a role in the modulation of many neurological pathways associated to drug addiction. In this context, the use of cannabinoids has been proposed as a therapeutic alternative for patients affected by cannabis use disorder. In a similar way nicotine replacement therapy is used as tobacco cessation strategy, it is postulated cannabinoids might help decrease abstinence and craving in cannabis abuse disorder.
Methods
To answer the question, we used Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a section of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence. |
We found seven systematic reviews [2],[3],[4],[5], |
|
What types of patients were included* |
Three trials [9],[11],[12] included adult patients with cannabis dependence according to DSM-IV-TR diagnostic criteria and one [10] included patients described as cannabis dependent recruited from the community without specifying diagnostic criteria. Three trials [9],[11],[12] excluded patients that had significant psychiatric comorbidities or other substance dependence (except for nicotine and caffeine) and one [10] did not specify exclusion criteria. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
Two trials evaluated nabiximol (Sativex) as intervention for 6 days [9] and for 9 weeks [10]. One trial [11] used oral dronabinol as monotherapy and another [12] used dronabinol associated with lofexidine (2-alpha adrenergic agonist). In one trial [9] both arms also received cognitive behavioral therapy. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The trials evaluated multiples outcomes, which were grouped by the different systematic reviews as follow:
|
* The information about primary studies is extracted from the systematic reviews identified, unless otherwise specified.
Summary of Findings
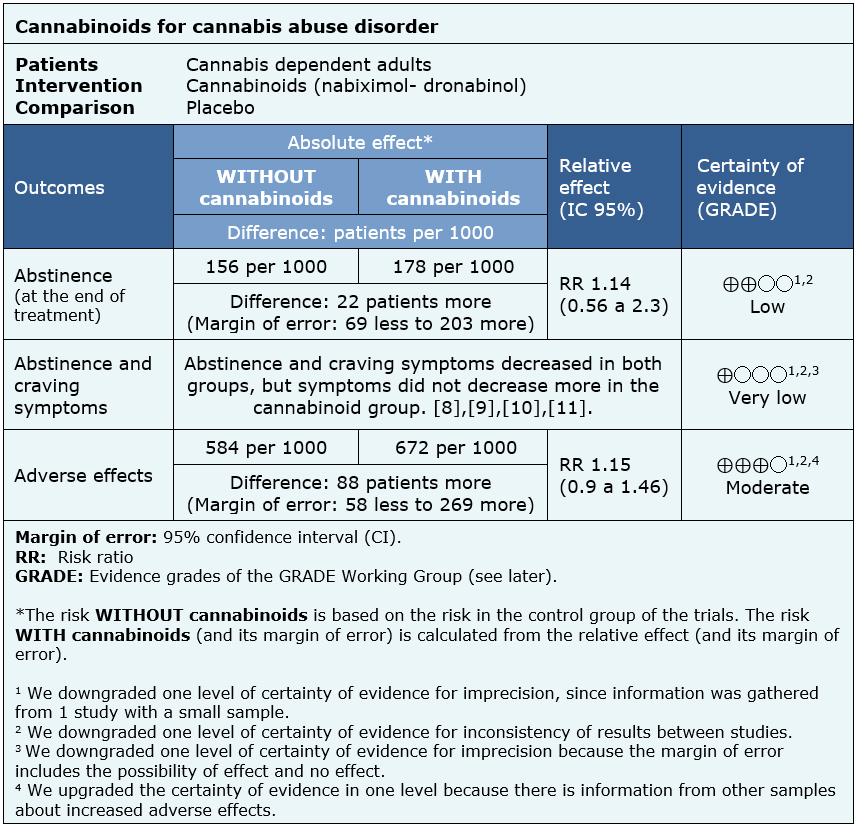
The information about the effects of cannabinoids is based on four randomized controlled trials including 338 patients [9],[10],[11],[12].
One trial reported abstinence at the end of treatment (156 patients) [11], four trials reported abstinence and craving symptoms (338 patients) [9],[10],[11],[12] and one trial reported adverse effects (156 patients) [11]. Regarding abstinence and craving symptoms, no systematic review allowed the extraction of data in a way that could be included in a meta analysis, so the information of this outcome is presented as a narrative synthesis.
The summary of findings is as follows:
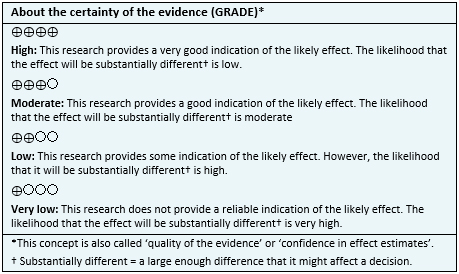
- The use of cannabinoids might result in little or no increase in abstinence at the end of treatment, but the certainty of the evidence is low.
- It is not clear if cannabinoids decrease abstinence and craving symptoms because the certainty of the evidence is very low.
- The use of cannabinoids probably increase adverse effects. The certainty of the evidence is moderate.
| Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings – iSoF) |
Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
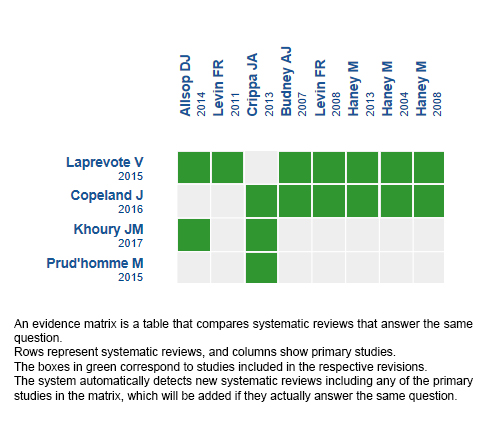
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Cannabinoids for cannabis use disorder
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.

