Resúmenes Epistemonikos
← vista completaPublicado el 29 de noviembre de 2019 | http://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2019.10.7727
Reconstrucción autóloga versus reconstrucción protésica para mujeres con cáncer de mama que serán sometidas a radioterapia post reconstrucción
Autologous versus prosthetic reconstruction for women with breast cancer who will undergo post-reconstruction radiotherapy
Abstract
INTRODUCTION Radiotherapy is frequently used after breast reconstruction in patients with locally advanced breast cancer or metastases in axillary lymph nodes. However, there might be differences between autologous and prosthetic reconstruction in terms of effectiveness and safety of post-reconstruction radiotherapy.
METHODS To answer this question we searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS We identified five systematic reviews including nine primary studies overall, of which all were observational studies. We concluded that in patients who will undergo post reconstructive radiotherapy, autologous breast reconstruction could reduce reoperations due to general complications compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction. However, it probably increases the risk of skin or flap necrosis. It is not clear whether there are differences in other outcomes as the certainty of evidence has been assessed as very low.
Problem
In 2017, 252,710 women were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer in the United States. It is estimated that over a third would undergo a total mastectomy, and 32% of them to breast reconstruction surgery [1],[2],[3]. There are two main techniques for breast reconstruction: autologous breast reconstruction with pedicled myocutaneous flaps or microsurgical free flaps, and prosthetic reconstruction, either with tissue expanders or definitive implants [4]. Once breast reconstruction has been conducted in locally advanced breast cancer or with metastatic involvement of axillary lymph nodes, it is common practice to apply radiotherapy, since it would reduce loco-regional recurrence and increase disease-free survival [5]. However, this can also negatively affect the results of breast reconstruction, with worse aesthetic results, need for post-radiation reoperation and even failure of breast reconstruction [6]. So, it has been proposed that depending on the type of breast reconstruction conducted prior to radiotherapy, different results could be obtained in relation to the final aesthetic reconstruction.
Methods
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence. |
We found five systematic reviews [6],[7],[8],[9],[10] that included nine primary studies overall [11],[12],[13],[14],[15],[16],[17],[18],[19], of which all corresponded to observational studies. Three non-comparative studies were excluded from this summary [12],[16],[18]. This table and general summary are based in six observational studies [11],[13],[14],[15],[17],[19] as no randomized trials were found that answered the question of interest. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
The effect of radiotherapy on breast reconstruction was evaluated for both groups. Six studies evaluated patients with post reconstructive radiotherapy [11],[13],[14],[15],[17],[19] and two of these studies also included patients with pre reconstruction radiotherapy [11],[15], whose subgroup was not considered for the analysis. No study described the average dose of radiotherapy used in patients. Two studies reported confusing potential variables such as body mass index, smoking habit or diabetes [11],[15], while four did not report it. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
In relation to breast reconstruction, three studies included patients with primary breast reconstruction [11],[15],[19] and three studies did not specify it [13],[14],[17]. In relation to type of reconstruction, six studies compared tissue expander/implant against autologous tissue. Of the latter, one study included autologous reconstruction with pedicled transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap [15], two studies included TRAM flap not specified [11],[19] and three studies did not reported the type of autologous reconstruction [13],[14],[17]. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The studies measured multiple outcomes that were organized by the systematic reviews as follows:
The average follow-up of the studies was 30 months with a range between 1 and 153 months. |
* The information about primary studies is extracted from the systematic reviews identified, unless otherwise specified.
Summary of findings
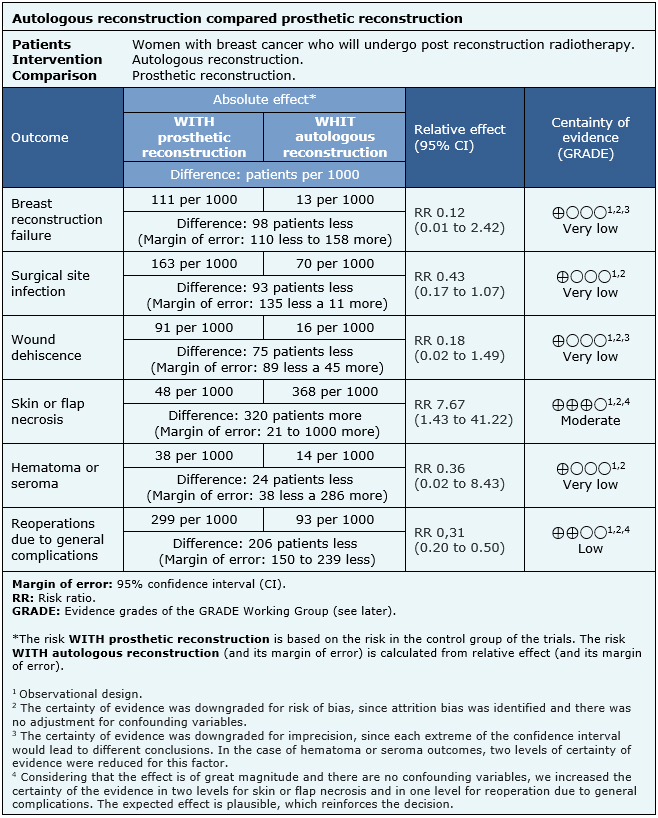
The information on the effects of autologous breast reconstruction versus prosthetic reconstruction in women with breast cancer who will undergo post reconstructive radiotherapy is based on six observational cohort studies including 478 patients in total.One study reported the outcome reconstruction failure (48 patients) [15], five studies reported surgical site infection (337 patients) [11],[13],[14],[15],[19], two studies reported wound dehiscence (98 patients) [15],[19], three studies reported skin or flap necrosis (183 patients) [11],[15],[19], one study reported hematoma or seroma (50 patients) [19] and five studies reported reoperation due to general complications (428 patients) [11],[13],[14],[15],[17].
The summary of findings is as follows:
- We are uncertain whether autologous breast reconstruction compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction reduces breast reconstruction failure in patients who underwent post reconstructive radiotherapy, as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
- We are uncertain whether autologous breast reconstruction compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction reduces surgical site infection in patients who underwent post reconstructive radiotherapy, as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
- We are uncertain whether autologous breast reconstruction compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction reduces wound dehiscence in patients who underwent post reconstructive radiotherapy, as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
- Autologous breast reconstruction compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction probably increases skin or flap necrosis in patients who underwent post reconstructive radiotherapy (moderate certainty of evidence).
- We are uncertain whether autologous breast reconstruction compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction reduces hematoma or seroma in patients who underwent post reconstructive radiotherapy, as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
- Autologous breast reconstruction compared to prosthetic breast reconstruction may reduce reoperations due to general complications in patients who underwent post reconstructive radiotherapy (low certainty of evidence).
|
Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings - iSoF) |
Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
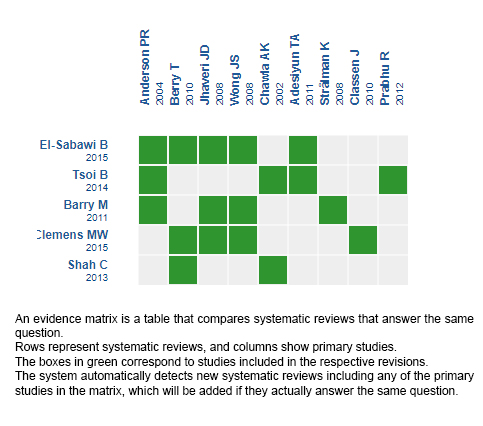
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Autologous reconstruction versus prosthetic reconstruction in women who will undergo radiotherapy post reconstruction.
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.

