Resúmenes Epistemonikos
← vista completaPublicado el 9 de diciembre de 2019 | http://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2019.11.7736
Acetazolamida como tratamiento del mal agudo de montaña
Acetazolamide for the treatment of acute mountain sickness
Abstract
INTRODUCTION Acute mountain sickness is the most prevalent illness related to acute exposure to high altitude, secondary to the hypobaric hypoxia effects in our body. Acetazolamide has been traditionally used for its prevention and treatment, however, there is still controversy regarding the degree of usefulness of this medication as monotherapy.
METHODS We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS We identified a systematic review that included two primary studies, both corresponding to randomized trials. We conclude that it is not possible to establish clearly whether treatment with acetazolamide reduces the symptoms of acute mountain disease or increases the risk of adverse effects, because the certainty of the existing evidence has been evaluated as very low.
Problem
When the organism is exposed to acute high-altitude hypobaric hypoxia, it develops a series of adaptive responses. However, if these responses are insufficient or abnormal, a spectrum of high-altitude illnesses that mainly include acute mountain sickness, high-altitude pulmonary edema and high-altitude cerebral edema, can occur. Of the three conditions previously indicated, acute mountain sickness is the most frequent, with its main symptoms being headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, sleep disturbances and anorexia [1].
For the prevention and treatment of this syndrome, a series of non-pharmacological and pharmacological measures have been used. One of them is acetazolamide, which inhibits the carbonic anhydrase enzyme at the renal level and causes urinary bicarbonate excretion and metabolic acidosis. Its effect triggers compensatory hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis, which promote the physiological response to the hypoxic stimulus. Despite being traditionally used, there is still controversy about the usefulness of acetazolamide as a treatment for acute mountain sickness[1].
Methods
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence. |
We found one systematic review [1], which included two primary studies [2], [3], both corresponding to randomized trials. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
Both trials included patients with acute mountain sickness, that is, subjects acutely exposed to high-altitude, presenting symptoms of headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, sleep disturbances and anorexia. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
Both trials evaluated the use of acetazolamide orally. One trial [2] administered 250 mg at 0 and 8 hours and the other [3] 20 mg/kg at baseline and then 500 mg daily for 5 days. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The trials reported multiple outcomes, which were grouped by systematic review as follows:
Primary outcomes:
|
* The information about primary studies is extracted from the systematic reviews identified, unless otherwise specified.
Summary of findings
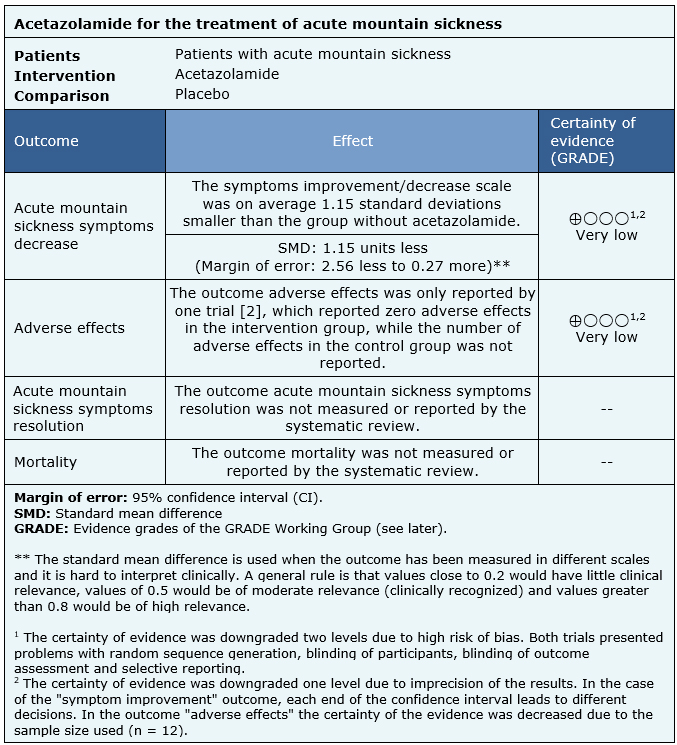
The information on the effects of acetazolamide for the treatment for acute mountain sickness is based on two randomized trials that included 25 patients.
Two trials reported acute mountain sickness symptoms decrease (25 patients) [2], [3], only one trial reported adverse effects, with incomplete results (12 patients) [2]. No trial reported the outcomes mortality or acute mountain sickness symptoms resolution.
The summary of findings is as follows:
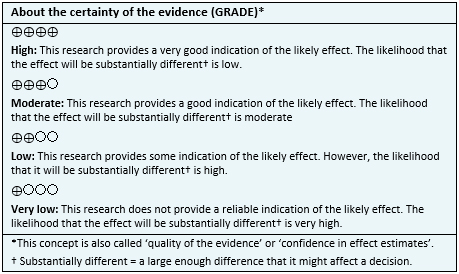
- We are uncertain whether treatment with acetazolamide decreases acute mountain sickness symptoms as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
- We are uncertain whether treatment with acetazolamide increases the risk of adverse effects as the certainty of the evidence has been assessed as very low.
- No studies were found to evaluate the reduction of mortality with treatment with acetazolamide.
- No studies were found to evaluate acute mountain sickness symptoms resolution with acetazolamide treatment.
| Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings – iSoF) |
Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
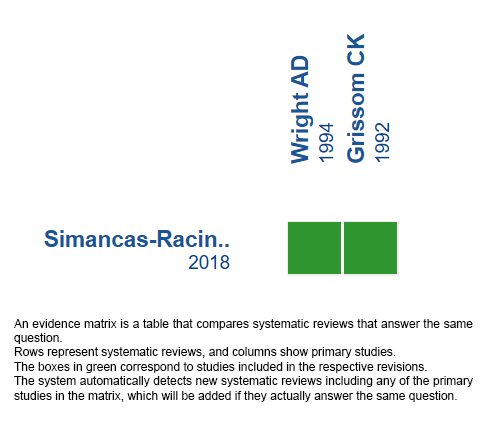
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Acetazolamide for the treatment of acute mountain syndrome.
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.

