Epistemonikos summaries
← vista completaPublished on January 16, 2020 | http://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2020.01.7759
Contralateral canes for knee osteoarthritis
Uso de bastones contralaterales en artrosis de rodilla
Abstract
Introduction Knee osteoarthritis is a relevant health problem given its high prevalence and associated disability. Within the non-pharmacological management alternatives, the use of canes has been proposed, however, there is no consensus in the literature regarding its indication.
Methods We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others. We extracted data from the systematic reviews, reanalyzed data of primary studies, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach.
Results and conclusions We identified three systematic reviews including four studies overall, of which one was randomized trials. We conclude that the use of a contralateral cane in patients with knee osteoarthritis probably reduces pain. In addition, it could slightly increase function, but the certainty of the evidence is low.
Problem
Osteoarthritis is a relevant health problem, with hip and knee osteoarthritis the eleventh leading cause of global disability, the thirty-eighth in years of life adjusted for disability[1] and an important reason for consultation in both primary and specialist care. Conservative management is the first line of treatment and its main objective is pain control. This includes the use of drugs, patient education, weight loss in patients with obesity, kinesiotherapy and the use of technical aids such as the cane, among others. The cane is used with the aim of reducing the biomechanical load that is exerted on the hip and knee. However, there is no consensus in the literature about its effect or its indication.
Methods
We searched in Epistemonikos, the largest database of systematic reviews in health, which is maintained by screening multiple information sources, including MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, among others, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. We extracted data from the identified reviews and reanalyzed data from primary studies included in those reviews. With this information, we generated a structured summary denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos) using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies when it is possible, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence See evidence matrix in Epistemonikos later |
We found three systematic reviews[2],[3],[4], which included four primary studies[5],[6],[7],[8] of which one corresponds to a randomized trial[7]. All the studies reported interesting outcomes, for which reason this table and the summary, in general, are based on these. |
|
What types of patients were included* |
All the studies[5],[6],[7],[8] included adult patients with a diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis, based on the American College of Rheumatology criteria, all of which presented symptoms (pain). The average age ranged from 53.6 to 65 years. 76.5% of the patients were women. |
|
What types of interventions were included* |
One study[5] evaluated the use of a contralateral walking pole, one trial[7] analyzed the use of a wooden cane with a contralateral T-shaped handle, the other two studies[6],[8] used contralateral cane not specifying the type. Three studies[5],[6], [8] compared the same patients without the use of canes, while one trial[7] compared a control group with knee osteoarthritis. |
|
What types of outcomes were measured |
Of the multiple outcomes measured by the trials, the systematic reviews presented in a grouped manner the following: pain, function, quality of life, walking speed, moment of adduction of the knee and vertical reaction force to the ground. The average follow-up of the trials was one month (range between 0 and 2 months). |
* Information about primary studies is not extracted directly from primary studies but from identified systematic reviews, unless otherwise stated.
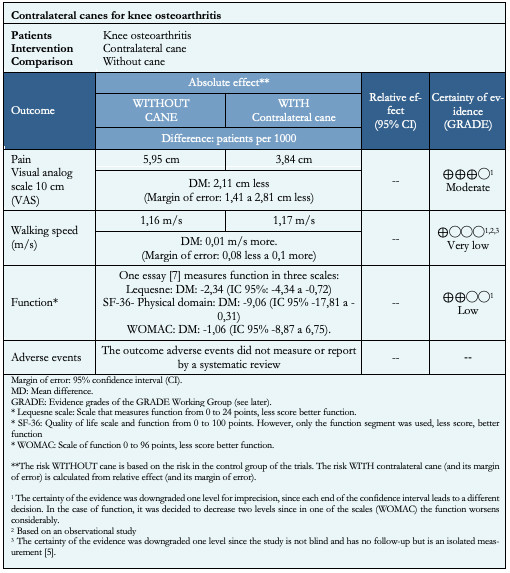
Summary of findings
The information on the effects of the use of canes in knee osteoarthritis is based on two studies, one observational[5] and one randomized[7], which included 98 patients.
The randomized trial[7] measured pain and function outcomes (64 patients), while the observational study[5] measured the walking speed outcome (34 patients).
The summary of the results is as follows:
-
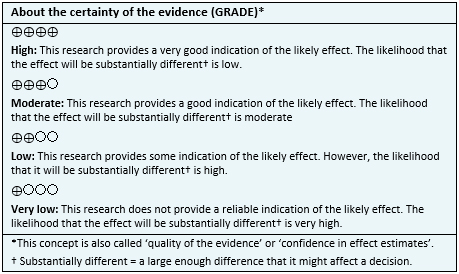
The use of contralateral cane in patients with knee osteoarthritis probably decreases the pain (certainty of the evidence is moderate).
-
It is not possible to establish clearly if contralateral cane use increases walking speed, because the certainty of the existing evidence has been evaluated as very low.
-
The use of a contralateral cane could slightly increase function (certainty of the evidence is low).
| Follow the link to access the interactive version of this table (Interactive Summary of Findings – iSoF) |
Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
| Differences between this summary and others sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
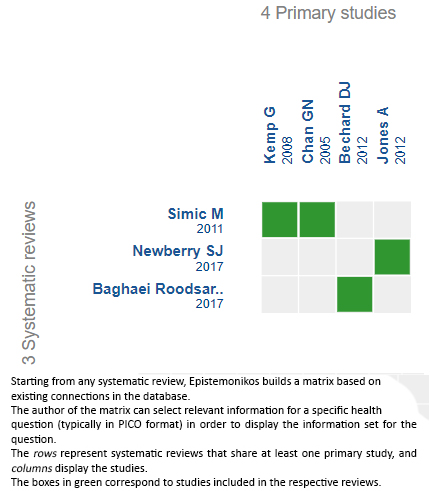
| Follow the link to access the interactive version: Canes for knee osteoarthritis |
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwaveor to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier.
After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
This article is part of the Epistemonikos Evidence Synthesis project. It is elaborated with a pre-established methodology, following rigorous methodological standards and internal peer review process. Each of these articles corresponds to a summary, denominated FRISBEE (Friendly Summary of Body of Evidence using Epistemonikos), whose main objective is to synthesize the body of evidence for a specific question, with a friendly format to clinical professionals. Its main resources are based on the evidence matrix of Epistemonikos and analysis of results using GRADE methodology. Further details of the methods for developing this FRISBEE are described here (http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997)
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
Potential conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.

