Resúmenes Epistemonikos
← vista completaPublicado el 10 de abril de 2017 | http://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2017.6918
¿Es efectivo el nintedanib para la fibrosis pulmonar idiopática?
Is nintedanib effective for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis has poor prognosis and effective therapies are scarce. In the search for treatments that can modify the course of the disease, nintedanib (BIBF 1120), a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has emerged as an alternative. However, its role is still unclear. To answer this question, we searched in Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple sources of information. We identified seven systematic reviews including seven randomized trials overall. We extracted data, conducted a meta-analysis and generated a summary of findings table using the GRADE approach. We concluded nintedanib probably decreases the risk of acute exacerbations, and might reduce mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. On the other hand, it is probably not associated with serious adverse events.
Problem
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a rare condition of unknown etiology [1]. The prognosis of this disease is poor and until the last decade, there were no interventions with a proven benefit on survival [2]. After diagnosis, survival decreases rapidly and factors such as acute exacerbations, time to disease progression and deterioration in respiratory functions are associated with a poorer prognosis [3],[4].
Nintedanib (BIBF 1120) is an inhibitor of multiple tyrosine kinase related signals through its binding to growth factor receptors. Among the most important are vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, fibroblast growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor [5]. An initial trial reported efficacy of this drug [6], which was later replicated, so the FDA approved this drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in 2015 [7],[8].
Methods
We used Epistemonikos database, which is maintained by screening multiple databases, to identify systematic reviews and their included primary studies. With this information, we generated a structured summary using a pre-established format, which includes key messages, a summary of the body of evidence (presented as an evidence matrix in Epistemonikos), meta-analysis of the total of studies, a summary of findings table following the GRADE approach and a table of other considerations for decision-making.
|
Key messages
|
About the body of evidence for this question
|
What is the evidence. |
We found seven systematic reviews, reported in eight references [9],[10],[11],[12],[13],[14],[15],[16] including seven randomized controlled trials reported in 10 references [6],[7],[17],[18],[19],[20],[21],[22],[23],[24]. |
|
What types of patients were included |
Three trials included patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis according to ATS / ERS 2011 criteria [6],[18],[19]. All of the trials included patients over 40 years of age. One trial included patients with PaO2 ≥55 mmHg at rest and room air, patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis within 5 years prior to enrollment and patients with high resolution computed tomography performed less than 1 year prior to enrollment [6]. Four trials included patients with functional vital capacity greater than or equal to 50% [6],[18],[19],[20]. Three trials included patients with a test of carbon monoxide diffusion capacity between 30% and 79% [6],[18],[19]. |
|
What types of interventions were included |
All of the trials used nintedanib as monotherapy at a dose of 300 mg daily. Three trials used an increasing dose of nintedanib until reaching the target dose of 300 mg daily [6],[20],[21]. All trials compared against placebo or standard treatment. |
|
What types of outcomes |
The different systematic reviews identified grouped the outcomes as follows:
|
Summary of findings
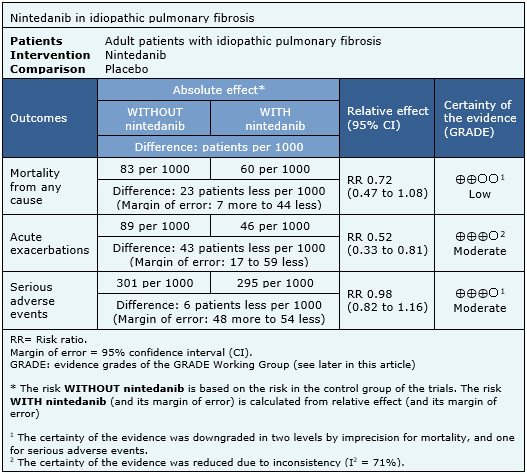
The information on the effects of nintedanib is based on three randomized trials [6],[18],[19] which included 1231 patients. The other four trials were not used in this analysis because they did not report enough data to be incorporated into a meta-analysis. All trials measured mortality, acute exacerbations, and serious adverse events. The summary of findings is as follows:
- Nintedanib might reduce mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The certainty of the evidence is low.
- Nintedanib probably decreases the risk of acute exacerbations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The certainty of the evidence is moderate.
- Nintedanib is probably not associated with serious adverse events. The certainty of the evidence is moderate.

Other considerations for decision-making
|
To whom this evidence does and does not apply |
|
| About the outcomes included in this summary |
|
| Balance between benefits and risks, and certainty of the evidence |
|
| What would patients and their doctors think about this intervention |
|
| Resource considerations |
|
|
Differences between this summary and other sources |
|
| Could this evidence change in the future? |
|
How we conducted this summary
Using automated and collaborative means, we compiled all the relevant evidence for the question of interest and we present it as a matrix of evidence.
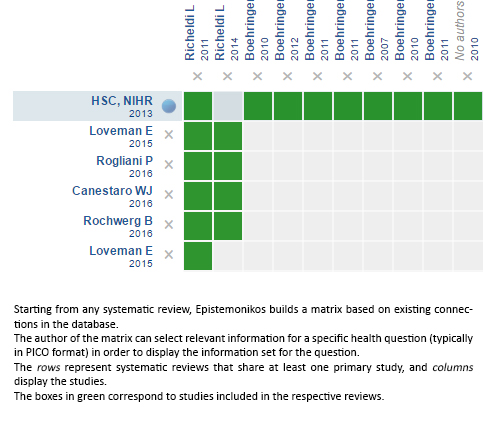
Follow the link to access the interactive version: Nintedanib for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Notes
The upper portion of the matrix of evidence will display a warning of “new evidence” if new systematic reviews are published after the publication of this summary. Even though the project considers the periodical update of these summaries, users are invited to comment in Medwave or to contact the authors through email if they find new evidence and the summary should be updated earlier. After creating an account in Epistemonikos, users will be able to save the matrixes and to receive automated notifications any time new evidence potentially relevant for the question appears.
The details about the methods used to produce these summaries are described here http://dx.doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2014.06.5997.
Epistemonikos foundation is a non-for-profit organization aiming to bring information closer to health decision-makers with technology. Its main development is Epistemonikos database (www.epistemonikos.org).
These summaries follow a rigorous process of internal peer review.
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have relevant interests to declare.

