Published on 24 de abril de 2023 | http://doi.org/10.5867/medwave.2023.03.2619
Effect of epigenetics on rheumatoid arthritis
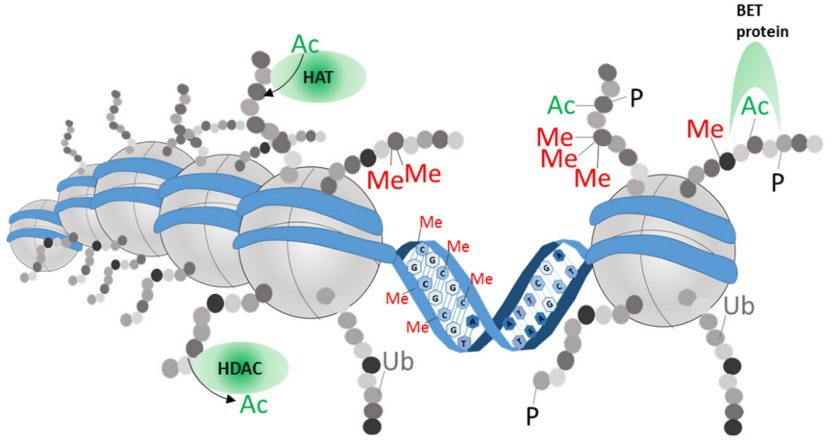
Epigenetic modifications.
DNA (blue) is coiled around histones (gray). Amino acid modifications to the protruding histone tails can influence DNA density and recruit repressor or transcriptional complexes. Histone marks are positioned, read, and removed by specialized enzymes. For example, histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) are shown. Bromo and extra-terminal domain (BET) family proteins bind to acetylated lysine on histone tails, after which they can promote transcription and recruitment of epigenetic enzymes to further stabilize the open chromatin state at a specific locus. Ac: acetylation, Me: methylation, P: phosphorylation, Ub: ubiquitination.